Strategic Risk Management
At Sumood, we enable organizations to make informed decisions and face the future with confidence, through advanced analytical and advisory solutions.
Enhancing Resilience and Ensuring Business Continuity
Organizations adopt a comprehensive strategy for resilience, preparedness, and adaptability by understanding their internal and external strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This is supported by:
- The availability of effective frameworks and governance for risk management, emergency response, and business continuity
- Effective emergency response plans and procedures, supported by scenarios and exercises
- Effective business continuity plans and procedures, including scenarios and exercises for business recovery
- A specialized team for risk management, emergency response, and business continuity, with expertise in identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks
- Collaboration with internal and external partners to develop and update risk mitigation strategies and ensure continuity of operations
- Access to best technical practices and emerging technologies for managing risks, emergencies, and business continuity
- A strong risk-aware culture and broad awareness among organization members
- Availability of training programs and resources for risk management, emergency preparedness, and business continuity
- The capability to conduct studies, perform analysis, and anticipate future scenarios
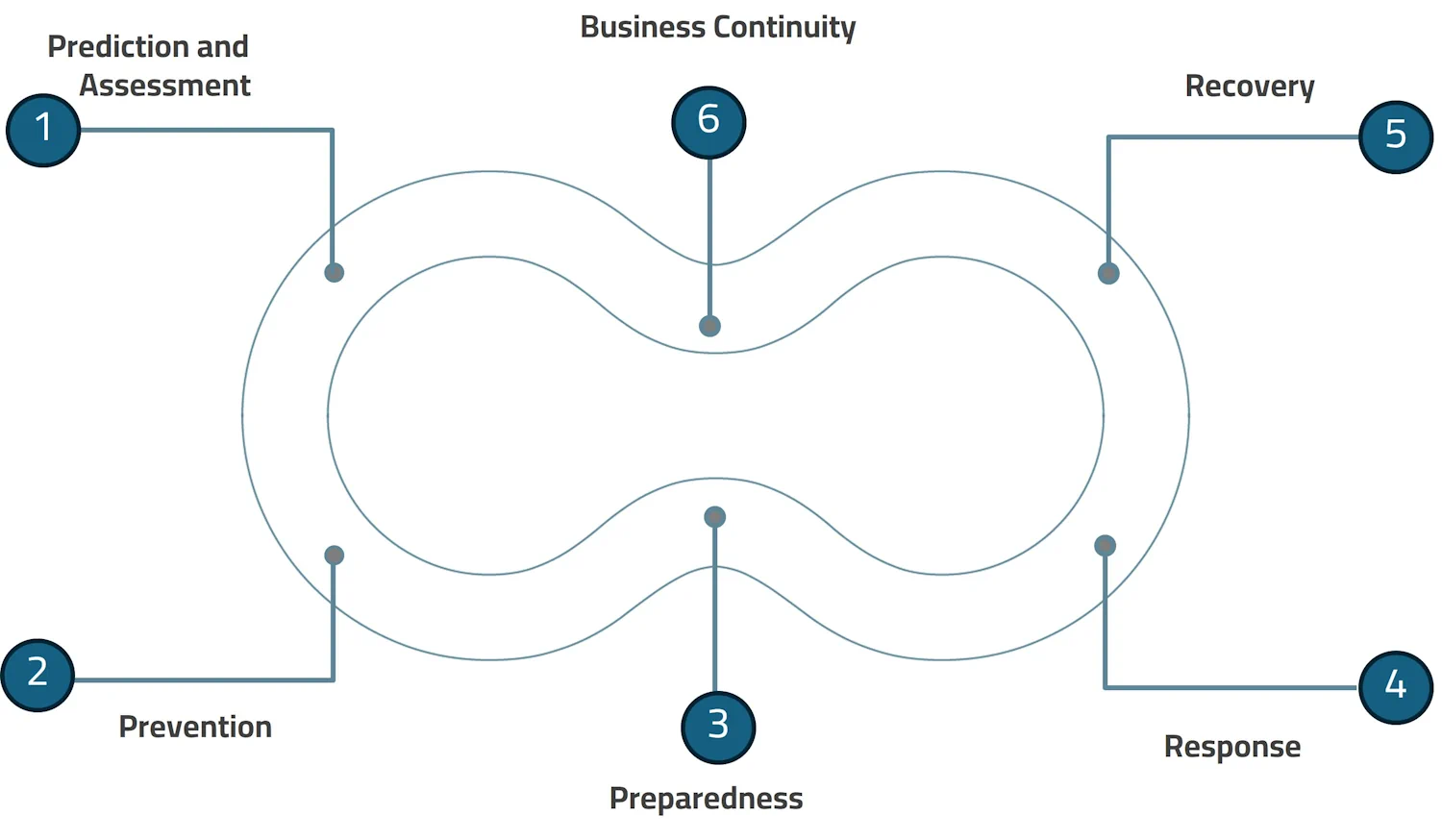
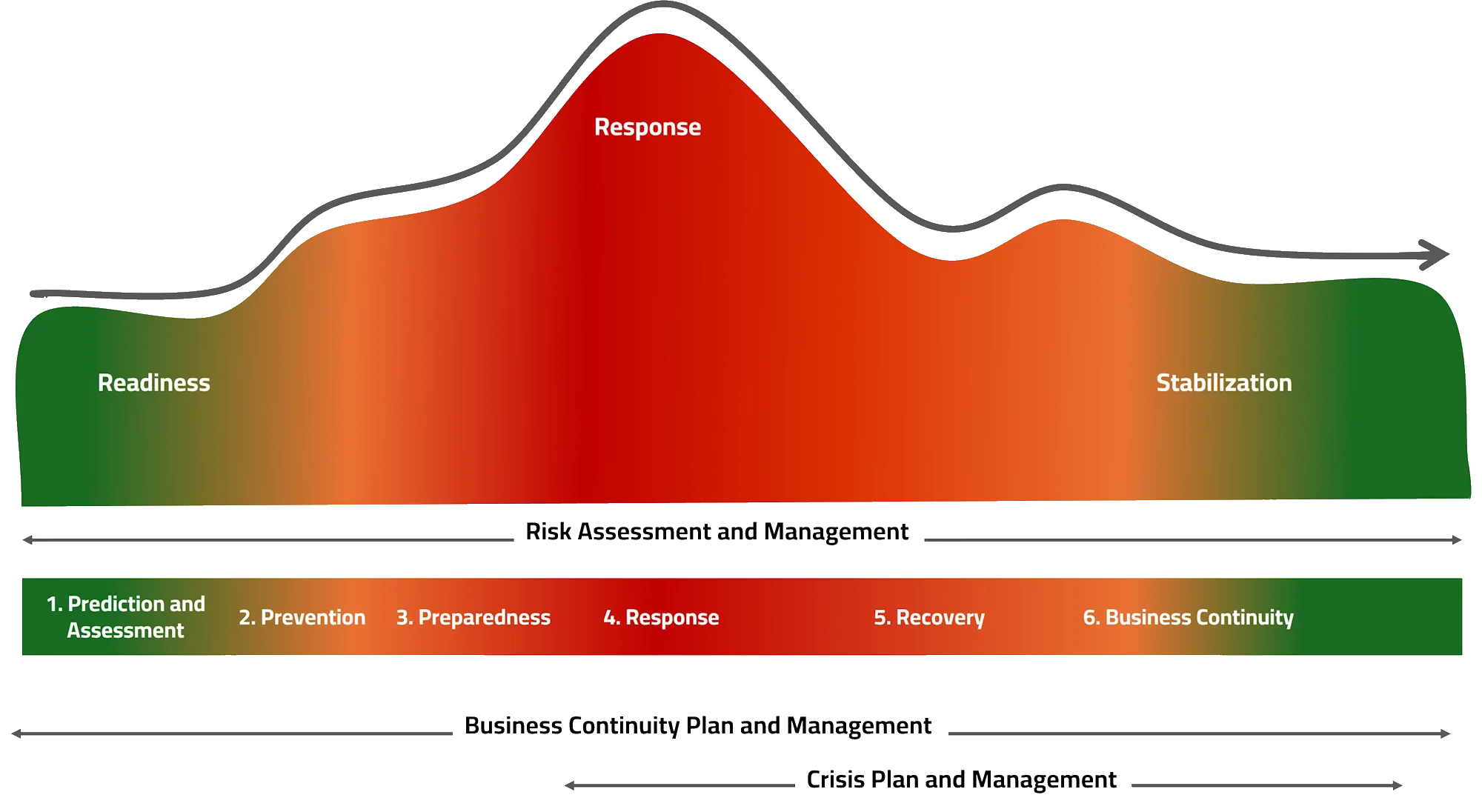
The business resilience cycle in any organization consists of three key phases: readiness, response, and stabilization.Risk management, emergency response, and business continuity are managed across all stages of the resilience cycle, including:
- Prediction and Assessment
- Prevention and mitigation
- Preparedness
- Response
- Recovery
- Business continuity
At Sumood, we help organizations build an integrated resilience system with effective frameworks and processes, guided by the goals of Saudi Vision 2030, the organization's strategic direction, the guidance of the National Risk Council of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, relevant laws, regulations, and international best practices.
To ensure the effectiveness of resilience management in any organization, we focus on building a comprehensive methodology for risk management, emergency preparedness, and business continuity, covering the following four main components:
- All Hazards
By having a dedicated risk management function responsible for identifying and assessing all potential risks that may face the organization and affect the achievement of its strategic, operational, financial objectives, or its reputation. This is based on historical, current, future, and emerging events and conditions.
- All Phases
By implementing risk management, emergency preparedness, and business continuity across all phases of the resilience cycle, including: anticipation and assessment, prevention and mitigation, preparedness, response, recovery, and business continuity.
- All Impacts
By studying, assessing, and addressing all expected impacts and consequences and their levels related to risks and their outcomes, such as emergencies, crises, or disasters. These impacts may affect: • Human life, safety, and health • Community well-being • Public and private properties • Continuity of critical infrastructure in delivering essential services and supplying vital goods • The Kingdom’s economy, resources, assets, and reputation • Public order • The environment and cultural heritage
- All Stakeholders
By establishing a comprehensive and effective governance system with clearly defined roles and responsibilities. This system ensures communication, coordination, cooperation, and integration, when needed, with all internal parties within the organization and all relevant external stakeholders.